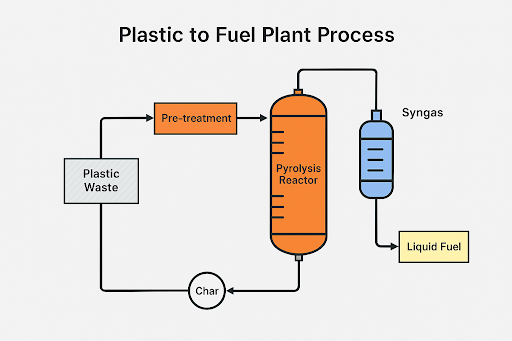
1. India – Small-Scale Modular Pyrolysis Plant (5 TPD)
Location: Gujarat, India
Operator: GreenEnvy Tech Pvt. Ltd.
Feedstock: Mixed post-consumer plastics (LDPE, HDPE, PP)
Key Features:
-
Modular skid-mounted design for rural deployment
-
Operates at 450–500°C under vacuum
-
Uses ceramic wool insulation and indirect heating via thermic oil
Performance:
-
Yield: 60–65% fuel oil, 20% gas, 10% char
-
Output used for internal diesel generator
-
Fully automated with PLC controls and gas recycling loop
Challenges:
-
Impurities in mixed waste required pre-washing unit
-
Catalyst fouling reduced yield after 4 months (solved by switching to alumino-silicate)
2. USA – Industrial Scale Plant (25 TPD)
Location: Ohio, USA
Operator: RES Polyflow (now Brightmark Energy)
Feedstock: LDPE films, mixed packaging waste, low-grade post-MRF residue
Key Features:
-
Horizontal rotary kiln pyrolysis
-
Operates in batch-mode with 8-hour cycles
-
Uses synthetic zeolite catalyst
-
Designed with integrated emission treatment (scrubber + activated carbon)
Performance:
-
Oil Yield: ~68%
-
100% of non-condensable gases reused for heating
-
End product certified as off-road diesel (ASTM D975-compliant)
Lessons Learned:
-
Proper size reduction critical for uniform heat transfer
-
Gas cleaning system needs daily maintenance for optimal VOC removal
3. Japan – Compact Urban Plant (10 TPD)
Location: Osaka, Japan
Operator: Blest Co. Ltd.
Feedstock: Clean HDPE & PP industrial waste
Key Features:
-
Compact design for urban siting
-
Fully enclosed system with odor control
-
Fast startup time: <2 hours
Outputs:
-
Fuel: Paraffinic oil used in small engines
-
Offgas: Compressed and bottled for use as backup fuel
-
Char: Sold as filler for asphalt products
Innovations:
-
Real-time process analytics (IR sensors)
-
CO₂-neutral cycle by integrating solar-powered heating
4. Kenya – Community-Based Plant (2 TPD)
Location: Kisumu, Kenya
Operator: EcoFuel Africa
Feedstock: Agricultural plastic waste and bags
Key Features:
-
Locally fabricated fixed-bed reactor
-
Manual loading and gravity discharge
-
Operated by women cooperatives as income generation
Products:
-
Oil used for powering irrigation pumps
-
Gas flared due to lack of storage system
-
Ash used in brick making
Social Impact:
-
Created 25+ jobs
-
Reduced open burning of plastic
-
Enabled clean water access through pump deployment
5. China – Co-Processing in Cement Kilns
Location: Shandong, China
Operator: SINOMA Cement Plant
Feedstock: Shredded mixed plastics (<50 mm)
Key Features:
-
No separate pyrolysis unit: plastics co-processed in cement kiln at >900°C
-
Energy recovered directly in clinker production
-
No fuel oil produced, but fossil fuel savings achieved
Benefits:
-
Replaces up to 10% coal input
-
No additional emissions (confirmed via stack testing)
-
Integrated into waste management plan of city
📊 Comparative Summary Table
|
Case |
Capacity |
Feedstock |
Yield
(Oil) |
Energy
Use |
Tech
Highlights |
|
India |
5 TPD |
Mixed plastics |
60–65% |
Thermic oil |
Modular, off-grid
ready |
|
USA |
25 TPD |
MRF residue |
~68% |
Gas reuse |
ASTM-grade diesel |
|
Japan |
10 TPD |
Clean HDPE/PP |
70% |
Low |
Urban setup, odor
control |
|
Kenya |
2 TPD |
Agri waste |
55% |
Biomass |
Community-led design |
|
China |
20–50 TPD |
Shredded mix |
N/A |
Kiln-integrated |
Co-processing, no
residue |
📝 Key Takeaways
-
Feedstock quality significantly influences oil yield and process stability.
-
Catalyst selection and pre-treatment are critical to long-term performance.
-
Automation and safety systems are vital, even at small scales.
-
Plants that integrate energy recycling and environmental controls achieve the best sustainability profiles.
-
Social impact and economic viability are major drivers in developing countries.